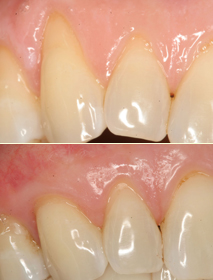
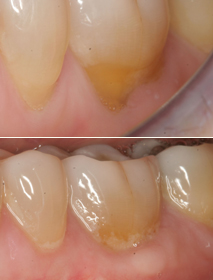
Steps in Identifying the Cause of Gum Recession
Receding gums are a condition where the gum tissue surrounding the teeth draws back or wears away. In doing so, the process reveals more of the tooth or tooth rot. Gum recession is a very common and correctable dental problem, and a significant reason for the prevalence of this condition is that most affected people are not aware of it, largely because the process occurs so gradually.
Why Do Gums Recede?
- Gum disease is the primary cause of gum recession.
- Genetics: More than 30 percent of all people are predisposed.
- Aggressive tooth brushing can damage the gums.
- Tobacco products cause it.
- Grinding or clenching of the teeth, especially during sleep, causes it.
Trust Your Oral Health to Top Periodontist,
Dr. Stephen Brown.
Offering minimally invasive treatment for gum disease
What Happens to My Gums Without Treatment?
- The gums will be increasingly sensitive and inflamed.
- The gums will become increasingly susceptible to disease-causing bacteria.
- Supporting tissue and bone structure will degrade.
How to Identify if Your Gums Are Receding
It is important to recognize that it may not be possible to identify receding gums based on visual evidence alone. Identification should start with regular checkups with a dentist. There are, however, signs that the person can look for to identify receding gums even before a dentist could.
Longer Teeth
Look at the teeth during each brushing. If they start to seem longer, then that may be an indication of recession, so set a dentist appointment as soon as possible.
Tooth Sensitivity
Increased sensitivity is usually one of the first symptoms of gum recession and other conditions. Never take sudden increased tooth sensitivity lightly.
Notch at the Gum Line
Feel where the gum meets the tooth. If there has been recession, then there will likely be a minor notch or indentation that is detectable by touch.
What Are My Options in Treating Receding Gums?
Prevention
Minor gum recession is reversible through prevention. Quit smoking. Take good care of the mouth consistently. Visit a dentist on a regular basis.
Antibiotics
If inflammation has occurred, then a dentist will prescribe antibiotics to combat it.
Deep Cleaning
A dentist can undo gum recession by performing a deep cleaning of the area where recession is occurring. This process includes scaling and root planning and the smoothing of any exposed root area.
Pocket Depth Reduction
During this process, the dentist removes the bacteria and then secures the receded gum back into place over the exposed root.
Regeneration
If there has been bone damage, then it is likely necessary to regenerate the lost bone and tissue. This process is similar to pocket depth reduction, but after folding back the receded skin, the dentist will use a regenerative material to stimulate the regrowth.
Soft Tissue Graft
Sometimes it is not possible to regenerate tissue. In this case, the dentist will perform a soft tissue graft. Usually, the dentist will take skin from the roof of the mouth and/or beneath the tongue to perform the graft.
To discover more regarding treating gum recession, contact us and schedule an appointment with Dr. I. Stephen Brown today!